Case Review
Four-dimensional flow magnetic resonance imaging study to explain high prevalence of pulmonary vein stump thrombus after left upper lobectomy
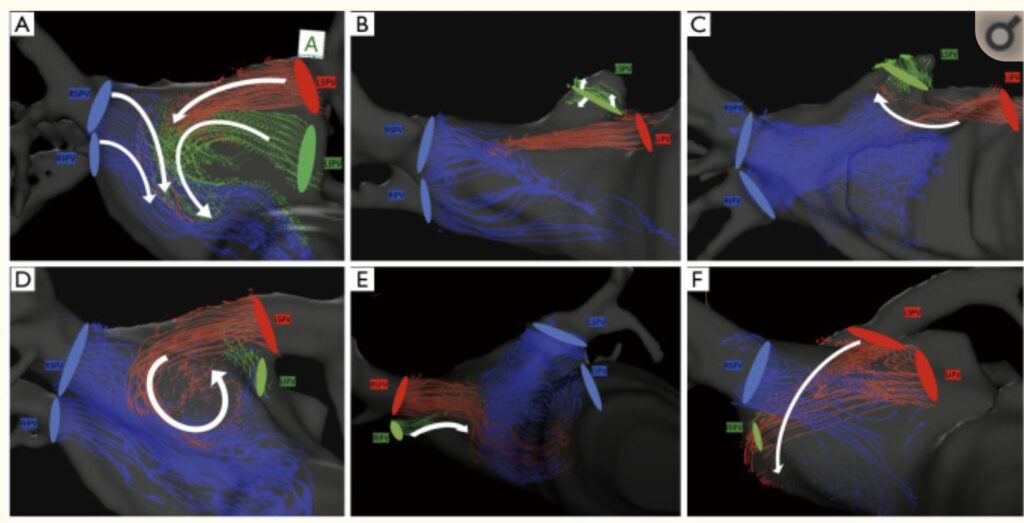
Pulmonary vein (PV) stump thrombus, a known source of cerebral infarction, develops almost exclusively after left upper lobectomy; however, the mechanism remains unclear.
They therefore evaluated the hemodynamics in the left atrium with four-dimensional flow magnetic resonance imaging (4D-flow MRI).
The result shows that their study revealed that left upper lobectomy likely causes blood turbulence near the vein stump through complicated blood streams in the left atrium, which can play a part in the development of vein stump thrombus.
They therefore evaluated the hemodynamics in the left atrium with four-dimensional flow magnetic resonance imaging (4D-flow MRI).
The result shows that their study revealed that left upper lobectomy likely causes blood turbulence near the vein stump through complicated blood streams in the left atrium, which can play a part in the development of vein stump thrombus.
Reference
Tadashi Umehara, Koji Takumi, Kazuhiro Ueda,Takuya Tokunaga, Aya Harada-Takeda, Soichi Suzuki, and Masami Sato, "Four-dimensional flow magnetic resonance imaging study to explain high prevalence of pulmonary vein stump thrombus after left upper lobectomy", Journal of Thoracic Disease , Published Online (2020) 10.21037/jtd-20-1606.
Go To the Journal Page

